EV Battery Working Principle | Electric Vehicle Battery
These days, Electric Cars (EV) are becoming more and more common. Because of this, the technology underlying the batteries that power EVs is becoming more and more significant. All owners desire to go great distances and swiftly charge their cars. As a result, multinational corporations (MNCs) like Tesla are attempting to create the most sophisticated and efficient EV batteries achievable. Prior to making an appointment to drive an EV, you should be aware of the main distinctions between gas- and electric-powered engines, the operation of the battery, and the future possibilities for EV batteries. Let’s review battery technologies specifically for electric vehicles.
Understanding The difference In IC Engine Vs EV Battery
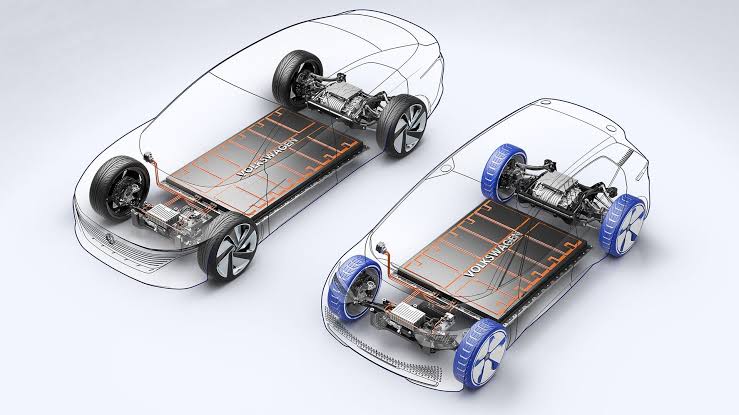
We are able to observe what powers our vehicle by taking a look under the hood. The fact has been proved that EV batteries are comparatively more efficient than internal combustion engines. Conventional cars have engines that run on the principle of combustion. Here, a spark plug ignites a pressurized fuel mixture to produce energy. This energy then drives the combustion chamber piston into action, which is then transferred to the crankshaft and causes the car’s wheels to spin in a circular pattern via a connecting rod. As a result, the car propels.
The procedure is completely different for electric vehicles. These cars can move and ignite without the need for gears to turn. So how does battery technology for electric vehicles operate? The controller uses the battery located beneath the hood of an EV to supply power to the internal motor. The wheels turn as a result of this action producing a magnetic force. By using fewer parts, this method produces more torque than conventional gas-powered cars. The vehicles accelerate quickly from 0 to 60 miles per hour because the battery’s electricity is sent directly to the wheels.
| Aspect | Electric Vehicle (Evs) | Internal Combustion Engine |
|---|---|---|
| Power Source | Electric motor powered by batteries or fuel cells | Combustion engine fueled by gasoline or diesel |
| Emission | Zero tailpipe emissions | Emissions of greenhouse gases and air pollutants |
| Fueling | Rechargeable batteries or hydrogen fuel cells | Gasoline, diesel, or alternative fuels |
| Driving Range | Typically lower range compared to ICE vehicles | Generally longer range depending on fuel tank capacity |
| Maintenance | Fewer moving parts, lower maintenance costs | More complex engine system, higher maintenance costs |
| Fueling Infrastructure | Growing network of charging stations | Well-established network of gas stations |
| Performance | Instant torque, smooth acceleration | Quick acceleration, high top speeds |
| Noise | Quiet operation | Engine noise during operation |
| Environmental Impact | Lower overall environmental impact | Higher emissions and ecological footprint |
| Cost of Ownership | Lower operating costs, higher upfront cost | Higher operating costs, lower upfront cost |
Battery Basics
1. The Power Pack
Picture this: EVs have a secret stash—a battery. Not just any battery—it’s like the Hulk version of your phone battery. We call it a lithium-ion battery. These bad boys store energy like squirrels hoard acorns. They sit under the car, chilling like a boss.
2. Charging Up
So, how do we juice up this battery? Imagine your EV at a charging station, sipping electrons like a fancy tea party. Plug it in, and voilà! The battery slurps up electricity faster than you can say “Tesla.”
3. Range Anxiety? Nah.
Once charged, your EV struts its stuff. It’s got a range, like a marathon runner. But instead of miles, we measure it in bananas (just kidding). Seriously, though, EVs can go far—some even cross-country. No more sweaty palms at the thought of running out of juice.
Electric Motor vs. Gas Engine
1. The Silent Whirr
Say hello to the electric motor. It’s the heart of your EV, purring like a contented cat. Unlike gas engines that go vroom-vroom, this motor whispers, “Let’s save the planet, shall we?” Smooth acceleration, no drama.
2. No Combustion Drama
Gas cars explode fuel to move. EVs? Nah. They’re chill. The motor spins, the wheels turn, and you glide silently. No smoke, no fuss. It’s like a spa day for your conscience.
Types of EV Batteries
Lithium-ion Battery: The most common battery type found in an electric vehicle is a lithium-ion battery. Mobile phones and other portable devices also use lithium-ion batteries. These batteries use extremely minimal electrical because they are lightweight. Additionally, these function incredibly well in hot environments.
Lead-Acid Batteries: These are less expensive and safer. Lead-acid batteries, on the other hand, have a limited lifespan and exhibit poor performance in cold climates. In the majority of EVs, they are utilized to store secondary power.
Nickel-Metal Hydride Batteries: The fuel in the car is needed to recharge these batteries. They require less upkeep and have a somewhat longer lifespan. On the other hand, they are expensive and quickly warm up in hot climates.
Types of Electric Vehicles
1. Battery Electric Vehicles (BEVs)
These are the true EV rockstars. They run solely on battery power. No gas, no compromises. Just pure electric goodness.
2. Hybrids
Think of hybrids as the veggie lovers of the EV world. They munch on electricity and sip a bit of gas. Best of both worlds, really.
3. Fuel Cell EVs (FCEVs)
These rebels use hydrogen. Yep, you heard right. They mix hydrogen with oxygen, throw a party, and—bam!—create electricity. It’s like science fiction, but real.
Steps to Increase Battery Life

You can take a number of actions to make sure the battery in your electric vehicle becomes exceptionally robust. Your EV battery can last anywhere from 13 to 15 years if you live in a moderate climate.
Whenever possible, drive your car at low speeds to preserve its battery. You can shorten the time it takes for the car to charge and conserve energy by doing this.
Parking your electric car in a shaded area is another option. High temperatures compel batteries to work harder, just as high speeds accelerate battery depletion. The vehicle employs its thermal management system to stay cool while parked directly in the sun. The vehicle’s battery is used to power this feature.
Final Verdict
Next time you see an EV zipping by, give it a nod. You know the secret handshake now. Whether you’re a tech geek or just curious, remember: EVs are the future, and they’re here to stay. So hop in, hit the pedal, and let’s ride toward a cleaner, quieter world. There are numerous steps for the Future technological advancements will undoubtedly lead to the development of newer, more advanced devices, which will have a big effect on the EV industry. Large corporations such as Tesla and Nissan are always striving to produce the greatest EV batteries they can in order to capture consumers’ attention. These batteries should provide greater levels of storage capacity together with increased range. The competition also includes smaller businesses like Nikola Motors. They are currently working on a battery that they claim would cut the charging time in half and increase the lifespan of an EV. Because of the market’s increased options and variable gasoline prices, EV adoption has already begun to increase. Furthermore, electric automobiles require less upkeep, and the most recent models even have longer driving ranges.
Join Us : WhatsApp Channel
Providing an overview of how electric vehicles operate and the fundamental principles of electric propulsion.
Contrasting the internal components and mechanics of electric vehicles with those of conventional gasoline-powered vehicles.
Explaining the sources of power for electric vehicles, such as batteries or fuel cells, and how electricity is stored for later use.
Describing the function of the electric motor in converting electrical energy into mechanical energy to propel the vehicle.
Discussing the different battery chemistries used in EVs and their impact on factors like performance, range, and charging time.
Explaining the concept of regenerative braking and how it allows electric vehicles to recover energy during deceleration and braking.
Detailing the various charging methods available for electric vehicles, including home charging, public charging stations, and fast charging, along with typical charging times.
Comparing pure electric vehicles (BEVs), plug-in hybrid electric vehicles (PHEVs), and hybrid electric vehicles (HEVs), and explaining how they function differently.
Highlighting the environmental advantages of electric vehicles, such as reduced greenhouse gas emissions and air pollution, and their contribution to sustainability.
Discussing the implications of ongoing technological advancements in electric vehicles for the future of transportation, energy consumption, and the automotive industry as a whole.